odontogenic keratocyst removal
The patient was evaluated after 15 days and the remaining sutures were removed. Removal of the cyst with removal of surrounding bone and or cryosurgery intense cold is applied to the cyst and bone are the most common forms of treatment.

Endoscopically Assisted Enucleation And Curettage Of Large Mandibular Odontogenic Keratocyst Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology And Endodontics
Numerous surgical methods have been practiced in the management of odontogenic keratocysts OKC.

. We discuss the outcome of 2 well-established and widely accepted methods used for the treatment of odontogenic keratocyst OKC enucleation with peripheral ostectomy or resection and decompression followed by enucleation and peripheral ostectomy. Cyst can be removed by open as well as endoscopic approach. Removal of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Maxilla Through the Le Fort I Osteotomy Authors.
Right Maxillary Sinus Mass Excision. Odontogenic tumors are a group of lesions with diverse histologic appearances and clinical behavior. Odontogenic tumours and cysts.
These diagnostic tools allow the dental professional to identify the type of cyst and plan appropriate treatment. We opted for an endoscopic approach because it offers minimal reductive change. Large odontogenic keratocysts sometimes are treated initially by cystotomy and insertion of a drainage tube which can promote shrinkage of the lesion and fibrous thickening of the cyst wall before subsequent total removal.
These methods are divided into conservative and aggressiveradical approaches or a combination of the two. Resection refers to either segmental resection surgical removal of a segment of the mandible or maxilla without maintaining the continuity of the bone or marginal resection surgical removal of a lesion intact with a rim of uninvolved bone maintaining the continuity of the bone 21 which is an extreme technique that results in considerable morbidity. Successful treatment therefore necessitates the complete removal of offending material and restoration or extraction of the tooth.
Odontogenic keratocyst are surgically removed by marsupialisation enucleation and chemical curettage with carnoys solution. Treatment of the odontogenic keratocyst involves meticulous resection to completely remove the lesion followed by reconstruction of the jaw with bone grafting. Odontogenic keratocysts OKC previously known as keratocystic odontogenic tumors KCOT or KOT are rare benign cystic lesions involving the mandible or maxilla and are believed to arise from dental lamina.
However much confusion still exists as to which methods provide the lowest recurrence rates RR without causing significant morbidity. The renaming of odontogenic keratocysts as keratocystic odontogenic tumors in 2005 then. The presentation can be unilocular or multilocular in appearance.
O Macedo Abstract The odontogenic keratocyst is a. Odontogenic keratocysts can initially be treated with incisional biopsy and decompression by installing a polyethylene drain to allow subsequent reduction of the cystic cavity size resulting in thickening of the capsule which allows a later easy removal withapparently lower relapse rate waldron. Long-term follow-up with monitoring by X-ray is important as if these cysts are left untreated they can become quite large and locally destructive.
If not secondary enucleation can be performed in better conditions. In rare instances particularly large cysts may require resection and bone grafting. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19 of jaw cysts.
Some are true neoplasms both benign and malignant and others are more likely hamartomas. Cysts are filled with keratinous debris. They may also suggest getting a biopsy where you will get part of the cyst removed and sent to a laboratory for further examination.
A mild pain was present since the past few. The patient has been followed up for 12 months with no signs of recurrence. Secondly it involves growth of a new OKC from small satellite cysts of odontogenic epithelial rests left behind by the surgical treatment.
- Consistent with odontogenic keratocyst benign ribbon-like squamous epithelium with keratinization separated from the underlying hyaline stroma with cartilage. The traditional method for the treatment of most KCOTs is surgical enucleation. An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cystIt most often affects the posterior mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life.
No complaints andor complications were reported. Nancy Herbst walks through how to properly remove an Odontogenic KeratocystLike and subscribe for moreUnion City Oral Surgery Group is located in Union. Dental professionals will typically recommend a test like an MRI CT or X-ray.
Odontogenic keratocysts are benign developmental cysts which cause extensive destruction of bone. The most common affection region is the posterior region of the lower jaw. Whether these lesions are developmental or neoplastic is controversial with the 2017 WHO classification placing it back into the.
The principle of treatment of odontogenic. The first reason involves incomplete removal of the original cysts lining. B Brancher L Cavalieri-Pereira G Pedroso-Oliveira C.
In the WHOIARC classification of head and neck pathology this clinical entity had been known for years as the odontogenic. The most commonly arise from the epithelial cell rests of the dental lamina. However due to the lining of the cyst being delicate and the fact that they frequently recur this method alone is not sufficient.
- NEGATIVE for malignancy. The diagnosis was odontogenic keratocyst. This 26-year-old man came to our hospital with a complaint of severe pain and swelling in his lower jaw left side.
A reduced volume to remove. Surgical Removal of Odontogenic Keratocyst. Implant surgery for the placement of dental implants is performed after full bony consolidation of the bone grafts to complete full oral rehabilitation for the patient.
The third reason involves the development of an unrelated OKC in an adjacent region of the jaws which is interpreted as a recurrence. - Benign respiratory mucosa with mild inflammation.

Review Of 5 Fluorouracil Is Associated With A Decreased Recurrence Risk In Odontogenic Keratocyst Management A Retrospective Cohort Study Journal Of Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery

Conservative Technique For Enucleation Of A Large Dentigerous Cyst Through Bony Fenestrations British Journal Of Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery
Odontogenic Keratocyst Okc Exodontia
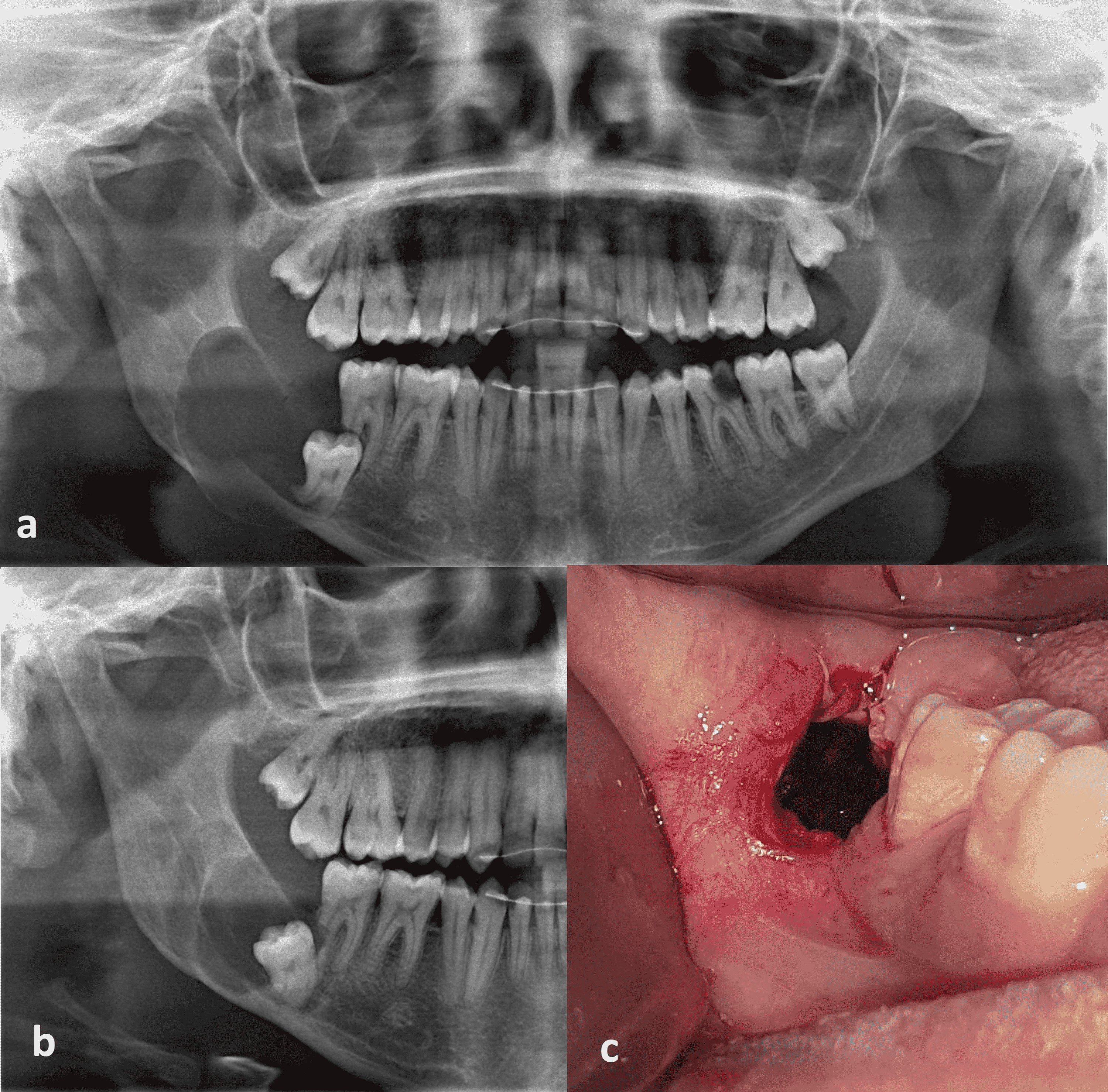
Cureus Marsupialization Of Dentigerous Cysts Followed By Enucleation And Extraction Of Deeply Impacted Third Molars A Report Of Two Cases

Role Of Carnoy S Solution As Treatment Adjunct In Jaw Lesions Other Than Odontogenic Keratocyst A Systematic Review British Journal Of Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery

Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor Treatment Modalities Study Of 3 Cases
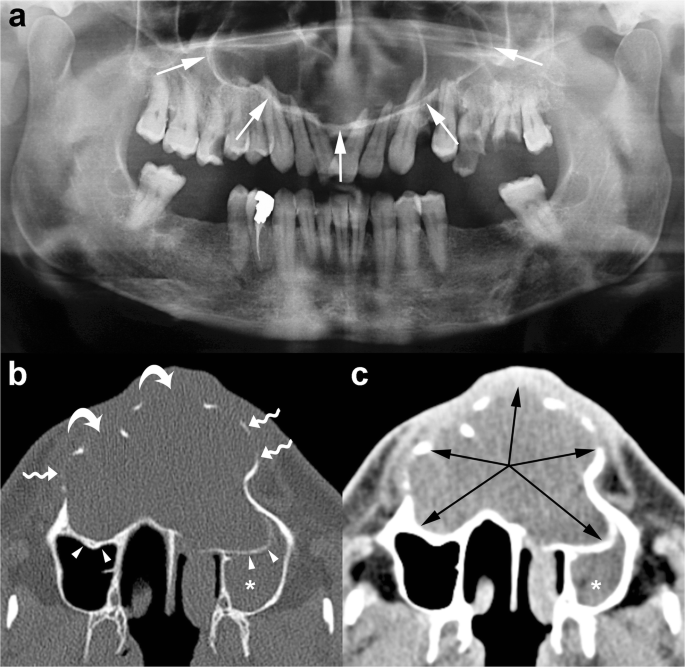
Odontogenic Keratocyst Imaging Features Of A Benign Lesion With An Aggressive Behaviour Springerlink

Recurrence Of Odontogenic Keratocyst Okc In Relation To Cortical Download Scientific Diagram
Odontogenic Keratocyst Okc Exodontia
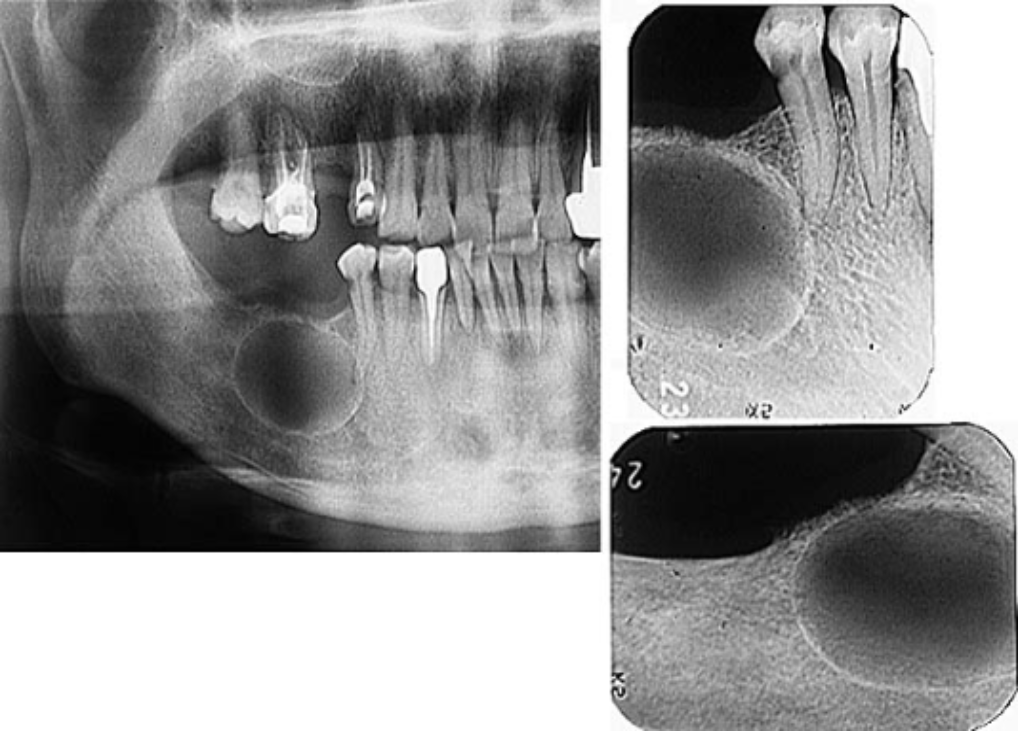
Odontogenic Keratocyst Okc Exodontia

Management Of Benign Odontogenic Lesions In The Paediatric Patient

Odontogenic Keratocyst R Radiology
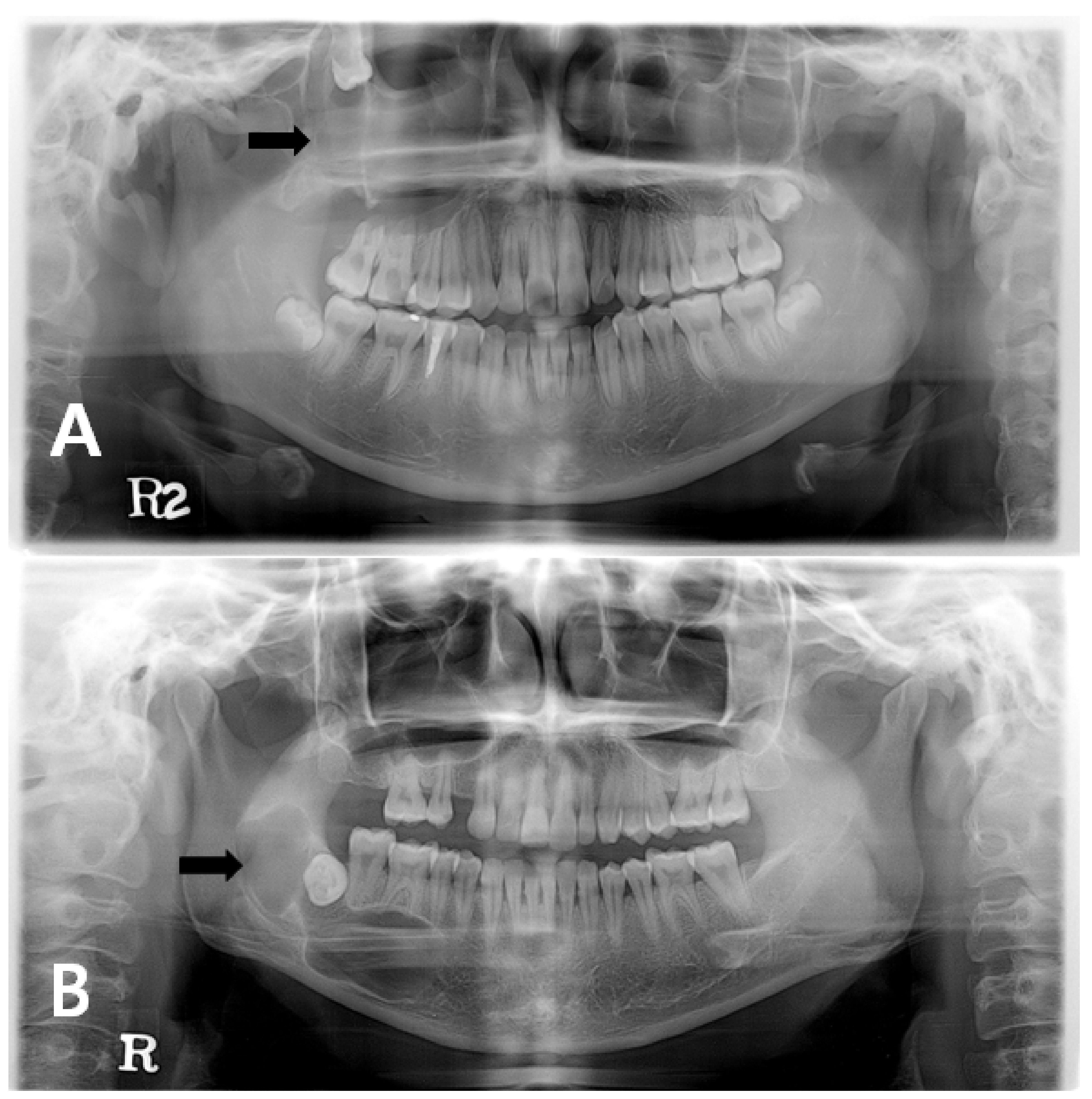
Jcm Free Full Text Changes In Cellular Regulatory Factors Before And After Decompression Of Odontogenic Keratocysts Html
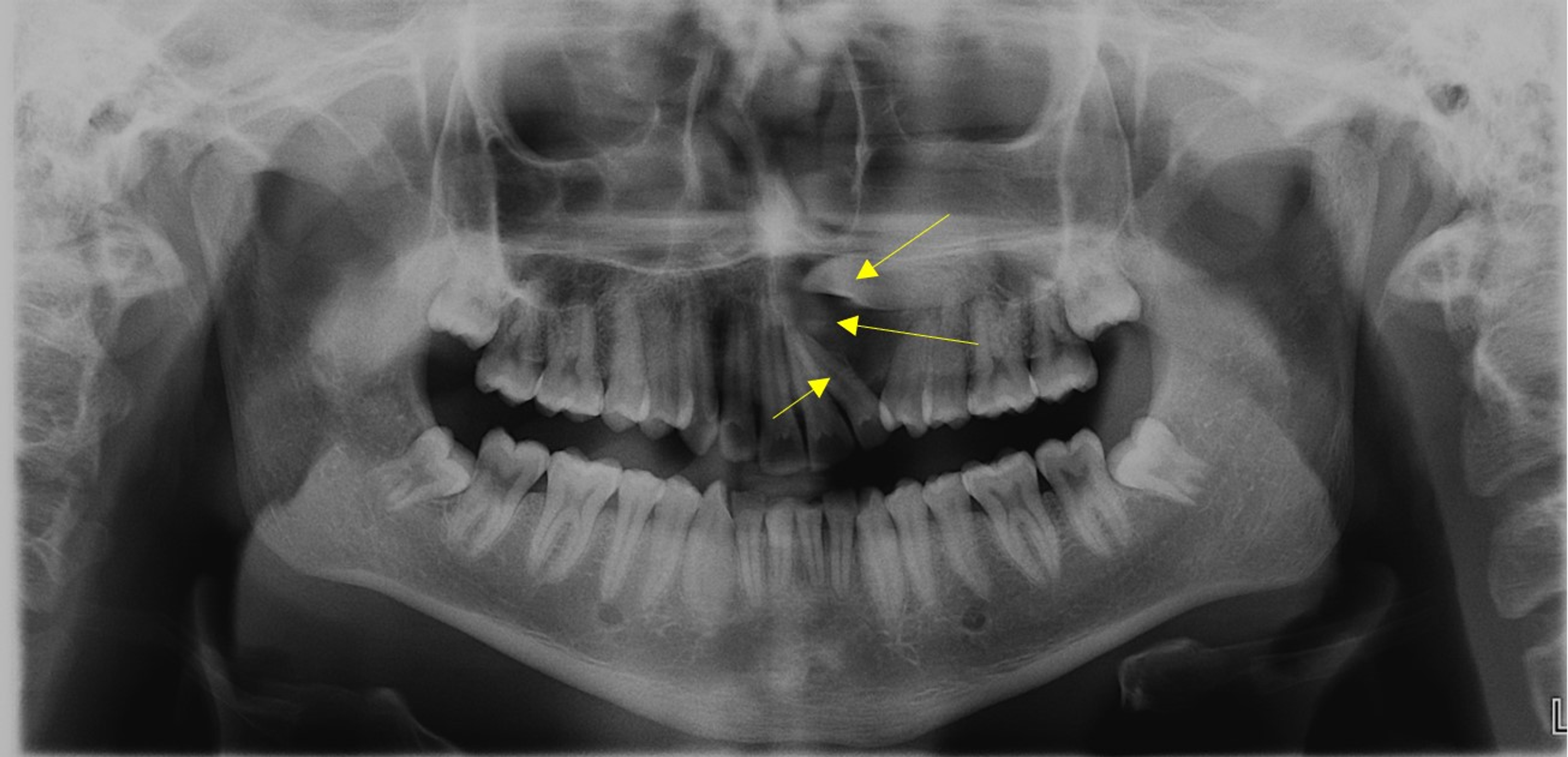
Cureus An Unusually Large Parakeratinised Odontogenic Keratocyst In The Maxilla With Extension Into The Floor Of The Maxillary Sinus

Pdf Removal Of Odontogenic Keratocyst In Maxilla Through The Le Fort I Osteotomy Semantic Scholar

Case Presentation Of A Patient Affected By Okc That Didn T Experience Download Scientific Diagram

Surgical Treatment Planning Several Mainly Conservative Approaches Have Been Suggested To The
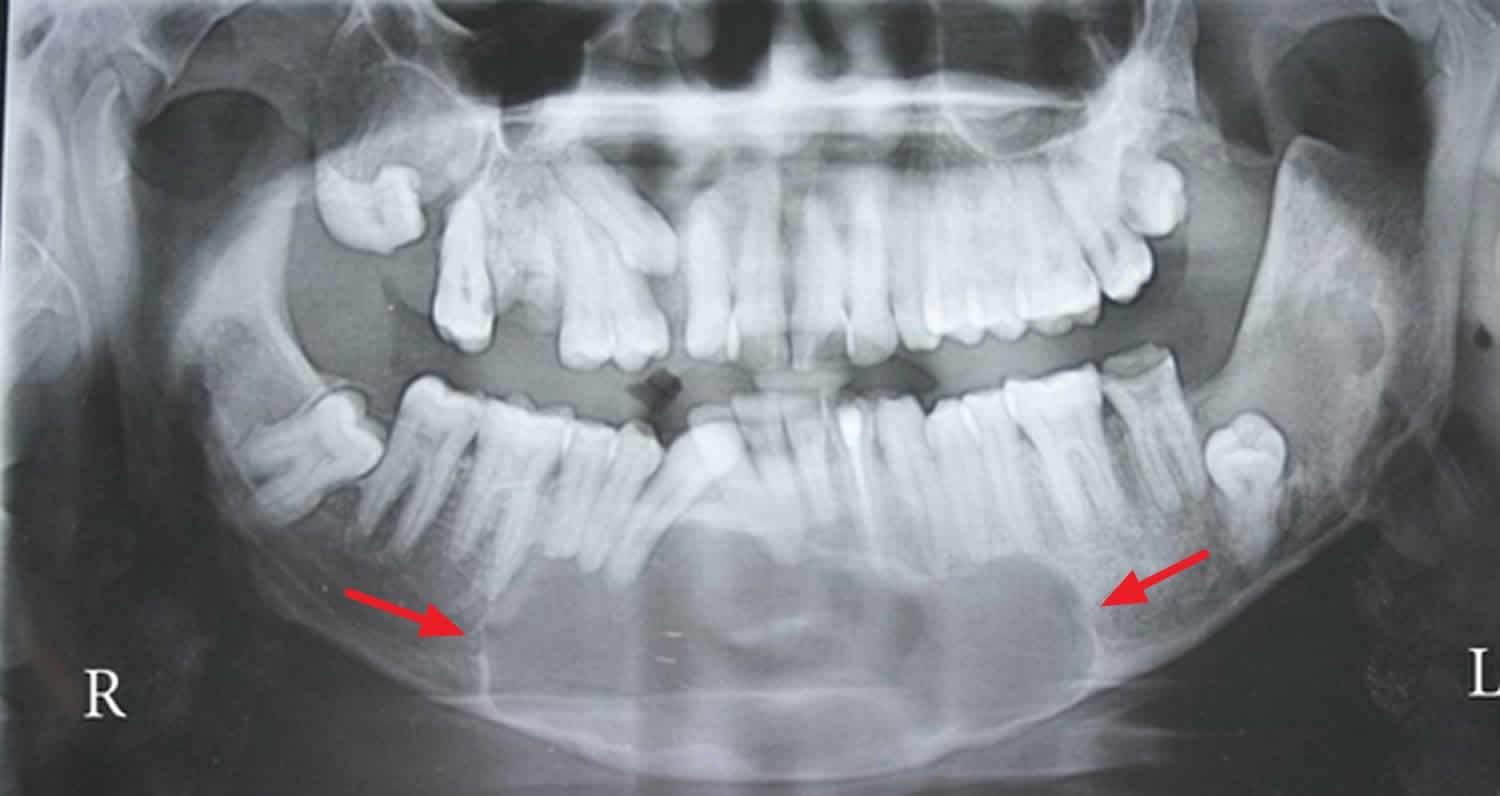
Odontogenic Keratocyst Definition Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis

Comments
Post a Comment